Prometheus는 Kafka Monitoring을 위한 도구입니다. helm을 이용하여 설치했으므로, helm이 설치되어 있는 것을 전제로 합니다.
1. 설치방법
1.helm으로 prometheus 설치
helm install --name air-kube-monitoring --namespace monitoring -f values.yaml stable/prometheus이때 사용한 values.yaml에서 가장 중요한 것은 외부 포트 오픈을 위해, server: service: type: NodePort를 지정하고, 이를 위한 nodePort를 지정해주었다는 것입니다. 또한 데이터 유지기간을 길게 잡기 위해서 retention을 365d로 주었습니다.
rbac:
create: true
podSecurityPolicy:
enabled: false
imagePullSecrets:
# - name: "image-pull-secret"
## Define serviceAccount names for components. Defaults to component's fully qualified name.
##
serviceAccounts:
alertmanager:
create: true
name:
kubeStateMetrics:
create: true
name:
nodeExporter:
create: true
name:
pushgateway:
create: true
name:
server:
create: true
name:
alertmanager:
## If false, alertmanager will not be installed
##
enabled: true
## alertmanager container name
##
name: alertmanager
## alertmanager container image
##
image:
repository: prom/alertmanager
tag: v0.18.0
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## alertmanager priorityClassName
##
priorityClassName: ""
## Additional alertmanager container arguments
##
extraArgs: {}
## The URL prefix at which the container can be accessed. Useful in the case the '-web.external-url' includes a slug
## so that the various internal URLs are still able to access as they are in the default case.
## (Optional)
prefixURL: ""
## External URL which can access alertmanager
## Maybe same with Ingress host name
baseURL: "/"
## Additional alertmanager container environment variable
## For instance to add a http_proxy
##
extraEnv: {}
## Additional alertmanager Secret mounts
# Defines additional mounts with secrets. Secrets must be manually created in the namespace.
extraSecretMounts: []
# - name: secret-files
# mountPath: /etc/secrets
# subPath: ""
# secretName: alertmanager-secret-files
# readOnly: true
## ConfigMap override where fullname is {{.Release.Name}}-{{.Values.alertmanager.configMapOverrideName}}
## Defining configMapOverrideName will cause templates/alertmanager-configmap.yaml
## to NOT generate a ConfigMap resource
##
configMapOverrideName: ""
## The name of a secret in the same kubernetes namespace which contains the Alertmanager config
## Defining configFromSecret will cause templates/alertmanager-configmap.yaml
## to NOT generate a ConfigMap resource
##
configFromSecret: ""
## The configuration file name to be loaded to alertmanager
## Must match the key within configuration loaded from ConfigMap/Secret
##
configFileName: alertmanager.yml
ingress:
## If true, alertmanager Ingress will be created
##
enabled: false
## alertmanager Ingress annotations
##
annotations: {}
# kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
# kubernetes.io/tls-acme: 'true'
## alertmanager Ingress additional labels
##
extraLabels: {}
## alertmanager Ingress hostnames with optional path
## Must be provided if Ingress is enabled
##
hosts: []
# - alertmanager.domain.com
# - domain.com/alertmanager
## Extra paths to prepend to every host configuration. This is useful when working with annotation based services.
extraPaths: []
# - path: /*
# backend:
# serviceName: ssl-redirect
# servicePort: use-annotation
## alertmanager Ingress TLS configuration
## Secrets must be manually created in the namespace
##
tls: []
# - secretName: prometheus-alerts-tls
# hosts:
# - alertmanager.domain.com
## Alertmanager Deployment Strategy type
# strategy:
# type: Recreate
## Node tolerations for alertmanager scheduling to nodes with taints
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/
##
tolerations: []
# - key: "key"
# operator: "Equal|Exists"
# value: "value"
# effect: "NoSchedule|PreferNoSchedule|NoExecute(1.6 only)"
## Node labels for alertmanager pod assignment
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/node-selection/
##
nodeSelector: {}
## Pod affinity
##
affinity: {}
## Use an alternate scheduler, e.g. "stork".
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/configure-multiple-schedulers/
##
# schedulerName:
persistentVolume:
## If true, alertmanager will create/use a Persistent Volume Claim
## If false, use emptyDir
##
enabled: true
## alertmanager data Persistent Volume access modes
## Must match those of existing PV or dynamic provisioner
## Ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/persistent-volumes/
##
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
## alertmanager data Persistent Volume Claim annotations
##
annotations: {}
## alertmanager data Persistent Volume existing claim name
## Requires alertmanager.persistentVolume.enabled: true
## If defined, PVC must be created manually before volume will be bound
existingClaim: ""
## alertmanager data Persistent Volume mount root path
##
mountPath: /data
## alertmanager data Persistent Volume size
##
size: 2Gi
## alertmanager data Persistent Volume Storage Class
## If defined, storageClassName: <storageClass>
## If set to "-", storageClassName: "", which disables dynamic provisioning
## If undefined (the default) or set to null, no storageClassName spec is
## set, choosing the default provisioner. (gp2 on AWS, standard on
## GKE, AWS & OpenStack)
##
# storageClass: "-"
## Subdirectory of alertmanager data Persistent Volume to mount
## Useful if the volume's root directory is not empty
##
subPath: ""
## Annotations to be added to alertmanager pods
##
podAnnotations: {}
## Specify if a Pod Security Policy for node-exporter must be created
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/
##
podSecurityPolicy:
annotations: {}
## Specify pod annotations
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/#apparmor
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/#seccomp
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/#sysctl
##
# seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/allowedProfileNames: '*'
# seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/defaultProfileName: 'docker/default'
# apparmor.security.beta.kubernetes.io/defaultProfileName: 'runtime/default'
## Use a StatefulSet if replicaCount needs to be greater than 1 (see below)
##
replicaCount: 1
statefulSet:
## If true, use a statefulset instead of a deployment for pod management.
## This allows to scale replicas to more than 1 pod
##
enabled: false
podManagementPolicy: OrderedReady
## Alertmanager headless service to use for the statefulset
##
headless:
annotations: {}
labels: {}
## Enabling peer mesh service end points for enabling the HA alert manager
## Ref: https://github.com/prometheus/alertmanager/blob/master/README.md
# enableMeshPeer : true
servicePort: 80
## alertmanager resource requests and limits
## Ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/compute-resources/
##
resources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: 10m
# memory: 32Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 10m
# memory: 32Mi
## Security context to be added to alertmanager pods
##
securityContext:
runAsUser: 65534
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsGroup: 65534
fsGroup: 65534
service:
annotations: {}
labels: {}
clusterIP: ""
## Enabling peer mesh service end points for enabling the HA alert manager
## Ref: https://github.com/prometheus/alertmanager/blob/master/README.md
# enableMeshPeer : true
## List of IP addresses at which the alertmanager service is available
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/services/#external-ips
##
externalIPs: []
loadBalancerIP: ""
loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
servicePort: 80
# nodePort: 30000
sessionAffinity: None
type: ClusterIP
## Monitors ConfigMap changes and POSTs to a URL
## Ref: https://github.com/jimmidyson/configmap-reload
##
configmapReload:
## configmap-reload container name
##
name: configmap-reload
## configmap-reload container image
##
image:
repository: jimmidyson/configmap-reload
tag: v0.2.2
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## Additional configmap-reload container arguments
##
extraArgs: {}
## Additional configmap-reload volume directories
##
extraVolumeDirs: []
## Additional configmap-reload mounts
##
extraConfigmapMounts: []
# - name: prometheus-alerts
# mountPath: /etc/alerts.d
# subPath: ""
# configMap: prometheus-alerts
# readOnly: true
## configmap-reload resource requests and limits
## Ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/compute-resources/
##
resources: {}
kubeStateMetrics:
## If false, kube-state-metrics will not be installed
##
enabled: true
## kube-state-metrics container name
##
name: kube-state-metrics
## kube-state-metrics container image
##
image:
repository: quay.io/coreos/kube-state-metrics
tag: v1.6.0
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## kube-state-metrics priorityClassName
##
priorityClassName: ""
## kube-state-metrics container arguments
##
args: {}
## Node tolerations for kube-state-metrics scheduling to nodes with taints
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/
##
tolerations: []
# - key: "key"
# operator: "Equal|Exists"
# value: "value"
# effect: "NoSchedule|PreferNoSchedule|NoExecute(1.6 only)"
## Node labels for kube-state-metrics pod assignment
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/node-selection/
##
nodeSelector: {}
## Annotations to be added to kube-state-metrics pods
##
podAnnotations: {}
## Specify if a Pod Security Policy for node-exporter must be created
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/
##
podSecurityPolicy:
annotations: {}
## Specify pod annotations
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/#apparmor
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/#seccomp
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/#sysctl
##
# seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/allowedProfileNames: '*'
# seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/defaultProfileName: 'docker/default'
# apparmor.security.beta.kubernetes.io/defaultProfileName: 'runtime/default'
pod:
labels: {}
replicaCount: 1
## kube-state-metrics resource requests and limits
## Ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/compute-resources/
##
resources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: 10m
# memory: 16Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 10m
# memory: 16Mi
## Security context to be added to kube-state-metrics pods
##
securityContext:
runAsUser: 65534
runAsNonRoot: true
service:
annotations:
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
labels: {}
# Exposed as a headless service:
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#headless-services
clusterIP: None
## List of IP addresses at which the kube-state-metrics service is available
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/services/#external-ips
##
externalIPs: []
loadBalancerIP: ""
loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
servicePort: 80
type: ClusterIP
nodeExporter:
## If false, node-exporter will not be installed
##
enabled: true
## If true, node-exporter pods share the host network namespace
##
hostNetwork: true
## If true, node-exporter pods share the host PID namespace
##
hostPID: true
## node-exporter container name
##
name: node-exporter
## node-exporter container image
##
image:
repository: prom/node-exporter
tag: v0.18.0
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## Specify if a Pod Security Policy for node-exporter must be created
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/
##
podSecurityPolicy:
annotations: {}
## Specify pod annotations
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/#apparmor
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/#seccomp
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/#sysctl
##
# seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/allowedProfileNames: '*'
# seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/defaultProfileName: 'docker/default'
# apparmor.security.beta.kubernetes.io/defaultProfileName: 'runtime/default'
## node-exporter priorityClassName
##
priorityClassName: ""
## Custom Update Strategy
##
updateStrategy:
type: RollingUpdate
## Additional node-exporter container arguments
##
extraArgs: {}
## Additional node-exporter hostPath mounts
##
extraHostPathMounts: []
# - name: textfile-dir
# mountPath: /srv/txt_collector
# hostPath: /var/lib/node-exporter
# readOnly: true
# mountPropagation: HostToContainer
extraConfigmapMounts: []
# - name: certs-configmap
# mountPath: /prometheus
# configMap: certs-configmap
# readOnly: true
## Node tolerations for node-exporter scheduling to nodes with taints
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/
##
tolerations: []
# - key: "key"
# operator: "Equal|Exists"
# value: "value"
# effect: "NoSchedule|PreferNoSchedule|NoExecute(1.6 only)"
## Node labels for node-exporter pod assignment
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/node-selection/
##
nodeSelector: {}
## Annotations to be added to node-exporter pods
##
podAnnotations: {}
## Labels to be added to node-exporter pods
##
pod:
labels: {}
## node-exporter resource limits & requests
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/compute-resources/
##
resources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: 200m
# memory: 50Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 100m
# memory: 30Mi
## Security context to be added to node-exporter pods
##
securityContext: {}
# runAsUser: 0
service:
annotations:
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
labels: {}
# Exposed as a headless service:
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#headless-services
clusterIP: None
## List of IP addresses at which the node-exporter service is available
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/services/#external-ips
##
externalIPs: []
hostPort: 9100
loadBalancerIP: ""
loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
servicePort: 9100
type: ClusterIP
server:
## Prometheus server container name
##
enabled: true
name: server
sidecarContainers:
## Prometheus server container image
##
image:
repository: prom/prometheus
tag: v2.13.1
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## prometheus server priorityClassName
##
priorityClassName: ""
## The URL prefix at which the container can be accessed. Useful in the case the '-web.external-url' includes a slug
## so that the various internal URLs are still able to access as they are in the default case.
## (Optional)
prefixURL: ""
## External URL which can access alertmanager
## Maybe same with Ingress host name
baseURL: ""
## Additional server container environment variables
##
## You specify this manually like you would a raw deployment manifest.
## This means you can bind in environment variables from secrets.
##
## e.g. static environment variable:
## - name: DEMO_GREETING
## value: "Hello from the environment"
##
## e.g. secret environment variable:
## - name: USERNAME
## valueFrom:
## secretKeyRef:
## name: mysecret
## key: username
env: {}
## This flag controls access to the administrative HTTP API which includes functionality such as deleting time
## series. This is disabled by default.
enableAdminApi: false
## This flag controls BD locking
skipTSDBLock: false
## Path to a configuration file on prometheus server container FS
configPath: /etc/config/prometheus.yml
global:
## How frequently to scrape targets by default
##
scrape_interval: 1m
## How long until a scrape request times out
##
scrape_timeout: 10s
## How frequently to evaluate rules
##
evaluation_interval: 1m
## Additional Prometheus server container arguments
##
extraArgs: {}
## Additional InitContainers to initialize the pod
##
extraInitContainers: []
## Additional Prometheus server Volume mounts
##
extraVolumeMounts: []
## Additional Prometheus server Volumes
##
extraVolumes: []
## Additional Prometheus server hostPath mounts
##
extraHostPathMounts: []
# - name: certs-dir
# mountPath: /etc/kubernetes/certs
# subPath: ""
# hostPath: /etc/kubernetes/certs
# readOnly: true
extraConfigmapMounts: []
# - name: certs-configmap
# mountPath: /prometheus
# subPath: ""
# configMap: certs-configmap
# readOnly: true
## Additional Prometheus server Secret mounts
# Defines additional mounts with secrets. Secrets must be manually created in the namespace.
extraSecretMounts: []
# - name: secret-files
# mountPath: /etc/secrets
# subPath: ""
# secretName: prom-secret-files
# readOnly: true
## ConfigMap override where fullname is {{.Release.Name}}-{{.Values.server.configMapOverrideName}}
## Defining configMapOverrideName will cause templates/server-configmap.yaml
## to NOT generate a ConfigMap resource
##
configMapOverrideName: ""
ingress:
## If true, Prometheus server Ingress will be created
##
enabled: false
## Prometheus server Ingress annotations
##
annotations: {}
# kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
# kubernetes.io/tls-acme: 'true'
## Prometheus server Ingress additional labels
##
extraLabels: {}
## Prometheus server Ingress hostnames with optional path
## Must be provided if Ingress is enabled
##
hosts: []
# - prometheus.domain.com
# - domain.com/prometheus
## Extra paths to prepend to every host configuration. This is useful when working with annotation based services.
extraPaths: []
# - path: /*
# backend:
# serviceName: ssl-redirect
# servicePort: use-annotation
## Prometheus server Ingress TLS configuration
## Secrets must be manually created in the namespace
##
tls: []
# - secretName: prometheus-server-tls
# hosts:
# - prometheus.domain.com
## Server Deployment Strategy type
# strategy:
# type: Recreate
## Node tolerations for server scheduling to nodes with taints
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/
##
tolerations: []
# - key: "key"
# operator: "Equal|Exists"
# value: "value"
# effect: "NoSchedule|PreferNoSchedule|NoExecute(1.6 only)"
## Node labels for Prometheus server pod assignment
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/node-selection/
##
nodeSelector: {}
## Pod affinity
##
affinity: {}
## Use an alternate scheduler, e.g. "stork".
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/configure-multiple-schedulers/
##
# schedulerName:
persistentVolume:
## If true, Prometheus server will create/use a Persistent Volume Claim
## If false, use emptyDir
##
enabled: true
## Prometheus server data Persistent Volume access modes
## Must match those of existing PV or dynamic provisioner
## Ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/persistent-volumes/
##
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
## Prometheus server data Persistent Volume annotations
##
annotations: {}
## Prometheus server data Persistent Volume existing claim name
## Requires server.persistentVolume.enabled: true
## If defined, PVC must be created manually before volume will be bound
existingClaim: ""
## Prometheus server data Persistent Volume mount root path
##
mountPath: /data
## Prometheus server data Persistent Volume size
##
size: 8Gi
## Prometheus server data Persistent Volume Storage Class
## If defined, storageClassName: <storageClass>
## If set to "-", storageClassName: "", which disables dynamic provisioning
## If undefined (the default) or set to null, no storageClassName spec is
## set, choosing the default provisioner. (gp2 on AWS, standard on
## GKE, AWS & OpenStack)
##
# storageClass: "-"
## Subdirectory of Prometheus server data Persistent Volume to mount
## Useful if the volume's root directory is not empty
##
subPath: ""
emptyDir:
sizeLimit: ""
## Annotations to be added to Prometheus server pods
##
podAnnotations: {}
# iam.amazonaws.com/role: prometheus
## Labels to be added to Prometheus server pods
##
podLabels: {}
## Specify if a Pod Security Policy for node-exporter must be created
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/
##
podSecurityPolicy:
annotations: {}
## Specify pod annotations
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/#apparmor
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/#seccomp
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/#sysctl
##
# seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/allowedProfileNames: '*'
# seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/defaultProfileName: 'docker/default'
# apparmor.security.beta.kubernetes.io/defaultProfileName: 'runtime/default'
## Use a StatefulSet if replicaCount needs to be greater than 1 (see below)
##
replicaCount: 1
statefulSet:
## If true, use a statefulset instead of a deployment for pod management.
## This allows to scale replicas to more than 1 pod
##
enabled: false
annotations: {}
labels: {}
podManagementPolicy: OrderedReady
## Alertmanager headless service to use for the statefulset
##
headless:
annotations: {}
labels: {}
servicePort: 80
## Prometheus server readiness and liveness probe initial delay and timeout
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-liveness-readiness-startup-probes/
##
readinessProbeInitialDelay: 30
readinessProbeTimeout: 30
livenessProbeInitialDelay: 30
livenessProbeTimeout: 30
## Prometheus server resource requests and limits
## Ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/compute-resources/
##
resources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: 500m
# memory: 512Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 500m
# memory: 512Mi
## Security context to be added to server pods
##
securityContext:
runAsUser: 65534
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsGroup: 65534
fsGroup: 65534
service:
annotations: {}
labels: {}
clusterIP: ""
## List of IP addresses at which the Prometheus server service is available
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/services/#external-ips
##
externalIPs: []
loadBalancerIP: ""
loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
servicePort: 80
sessionAffinity: None
type: NodePort
nodePort: 30090
## Prometheus server pod termination grace period
##
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 300
## Prometheus data retention period (default if not specified is 15 days)
##
retention: "365d"
pushgateway:
## If false, pushgateway will not be installed
##
enabled: true
## Use an alternate scheduler, e.g. "stork".
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/configure-multiple-schedulers/
##
# schedulerName:
## pushgateway container name
##
name: pushgateway
## pushgateway container image
##
image:
repository: prom/pushgateway
tag: v0.8.0
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## pushgateway priorityClassName
##
priorityClassName: ""
## Additional pushgateway container arguments
##
## for example: persistence.file: /data/pushgateway.data
extraArgs: {}
ingress:
## If true, pushgateway Ingress will be created
##
enabled: false
## pushgateway Ingress annotations
##
annotations: {}
# kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
# kubernetes.io/tls-acme: 'true'
## pushgateway Ingress hostnames with optional path
## Must be provided if Ingress is enabled
##
hosts: []
# - pushgateway.domain.com
# - domain.com/pushgateway
## Extra paths to prepend to every host configuration. This is useful when working with annotation based services.
extraPaths: []
# - path: /*
# backend:
# serviceName: ssl-redirect
# servicePort: use-annotation
## pushgateway Ingress TLS configuration
## Secrets must be manually created in the namespace
##
tls: []
# - secretName: prometheus-alerts-tls
# hosts:
# - pushgateway.domain.com
## Node tolerations for pushgateway scheduling to nodes with taints
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/
##
tolerations: []
# - key: "key"
# operator: "Equal|Exists"
# value: "value"
# effect: "NoSchedule|PreferNoSchedule|NoExecute(1.6 only)"
## Node labels for pushgateway pod assignment
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/node-selection/
##
nodeSelector: {}
## Annotations to be added to pushgateway pods
##
podAnnotations: {}
## Specify if a Pod Security Policy for node-exporter must be created
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/
##
podSecurityPolicy:
annotations: {}
## Specify pod annotations
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/#apparmor
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/#seccomp
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/#sysctl
##
# seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/allowedProfileNames: '*'
# seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/defaultProfileName: 'docker/default'
# apparmor.security.beta.kubernetes.io/defaultProfileName: 'runtime/default'
replicaCount: 1
## pushgateway resource requests and limits
## Ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/compute-resources/
##
resources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: 10m
# memory: 32Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 10m
# memory: 32Mi
## Security context to be added to push-gateway pods
##
securityContext:
runAsUser: 65534
runAsNonRoot: true
service:
annotations:
prometheus.io/probe: pushgateway
labels: {}
clusterIP: ""
## List of IP addresses at which the pushgateway service is available
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/services/#external-ips
##
externalIPs: []
loadBalancerIP: ""
loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
servicePort: 9091
type: ClusterIP
## pushgateway Deployment Strategy type
# strategy:
# type: Recreate
persistentVolume:
## If true, pushgateway will create/use a Persistent Volume Claim
## If false, use emptyDir
##
enabled: false
## pushgateway data Persistent Volume access modes
## Must match those of existing PV or dynamic provisioner
## Ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/persistent-volumes/
##
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
## pushgateway data Persistent Volume Claim annotations
##
annotations: {}
## pushgateway data Persistent Volume existing claim name
## Requires pushgateway.persistentVolume.enabled: true
## If defined, PVC must be created manually before volume will be bound
existingClaim: ""
## pushgateway data Persistent Volume mount root path
##
mountPath: /data
## pushgateway data Persistent Volume size
##
size: 2Gi
## alertmanager data Persistent Volume Storage Class
## If defined, storageClassName: <storageClass>
## If set to "-", storageClassName: "", which disables dynamic provisioning
## If undefined (the default) or set to null, no storageClassName spec is
## set, choosing the default provisioner. (gp2 on AWS, standard on
## GKE, AWS & OpenStack)
##
# storageClass: "-"
## Subdirectory of alertmanager data Persistent Volume to mount
## Useful if the volume's root directory is not empty
##
subPath: ""
## alertmanager ConfigMap entries
##
alertmanagerFiles:
alertmanager.yml:
global: {}
# slack_api_url: ''
receivers:
- name: default-receiver
# slack_configs:
# - channel: '@you'
# send_resolved: true
route:
group_wait: 10s
group_interval: 5m
receiver: default-receiver
repeat_interval: 3h
## Prometheus server ConfigMap entries
##
serverFiles:
## Alerts configuration
## Ref: https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/alerting_rules/
alerts: {}
# groups:
# - name: Instances
# rules:
# - alert: InstanceDown
# expr: up == 0
# for: 5m
# labels:
# severity: page
# annotations:
# description: '{{ $labels.instance }} of job {{ $labels.job }} has been down for more than 5 minutes.'
# summary: 'Instance {{ $labels.instance }} down'
rules: {}
prometheus.yml:
rule_files:
- /etc/config/rules
- /etc/config/alerts
scrape_configs:
- job_name: prometheus
static_configs:
- targets:
- localhost:9090
# A scrape configuration for running Prometheus on a Kubernetes cluster.
# This uses separate scrape configs for cluster components (i.e. API server, node)
# and services to allow each to use different authentication configs.
#
# Kubernetes labels will be added as Prometheus labels on metrics via the
# `labelmap` relabeling action.
# Scrape config for API servers.
#
# Kubernetes exposes API servers as endpoints to the default/kubernetes
# service so this uses `endpoints` role and uses relabelling to only keep
# the endpoints associated with the default/kubernetes service using the
# default named port `https`. This works for single API server deployments as
# well as HA API server deployments.
- job_name: 'kubernetes-apiservers'
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
# Default to scraping over https. If required, just disable this or change to
# `http`.
scheme: https
# This TLS & bearer token file config is used to connect to the actual scrape
# endpoints for cluster components. This is separate to discovery auth
# configuration because discovery & scraping are two separate concerns in
# Prometheus. The discovery auth config is automatic if Prometheus runs inside
# the cluster. Otherwise, more config options have to be provided within the
# <kubernetes_sd_config>.
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
# If your node certificates are self-signed or use a different CA to the
# master CA, then disable certificate verification below. Note that
# certificate verification is an integral part of a secure infrastructure
# so this should only be disabled in a controlled environment. You can
# disable certificate verification by uncommenting the line below.
#
insecure_skip_verify: true
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
# Keep only the default/kubernetes service endpoints for the https port. This
# will add targets for each API server which Kubernetes adds an endpoint to
# the default/kubernetes service.
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace, __meta_kubernetes_service_name, __meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name]
action: keep
regex: default;kubernetes;https
- job_name: 'kubernetes-nodes'
# Default to scraping over https. If required, just disable this or change to
# `http`.
scheme: https
# This TLS & bearer token file config is used to connect to the actual scrape
# endpoints for cluster components. This is separate to discovery auth
# configuration because discovery & scraping are two separate concerns in
# Prometheus. The discovery auth config is automatic if Prometheus runs inside
# the cluster. Otherwise, more config options have to be provided within the
# <kubernetes_sd_config>.
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
# If your node certificates are self-signed or use a different CA to the
# master CA, then disable certificate verification below. Note that
# certificate verification is an integral part of a secure infrastructure
# so this should only be disabled in a controlled environment. You can
# disable certificate verification by uncommenting the line below.
#
insecure_skip_verify: true
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: node
relabel_configs:
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+)
- target_label: __address__
replacement: kubernetes.default.svc:443
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_name]
regex: (.+)
target_label: __metrics_path__
replacement: /api/v1/nodes/$1/proxy/metrics
- job_name: 'kubernetes-nodes-cadvisor'
# Default to scraping over https. If required, just disable this or change to
# `http`.
scheme: https
# This TLS & bearer token file config is used to connect to the actual scrape
# endpoints for cluster components. This is separate to discovery auth
# configuration because discovery & scraping are two separate concerns in
# Prometheus. The discovery auth config is automatic if Prometheus runs inside
# the cluster. Otherwise, more config options have to be provided within the
# <kubernetes_sd_config>.
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
# If your node certificates are self-signed or use a different CA to the
# master CA, then disable certificate verification below. Note that
# certificate verification is an integral part of a secure infrastructure
# so this should only be disabled in a controlled environment. You can
# disable certificate verification by uncommenting the line below.
#
insecure_skip_verify: true
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: node
# This configuration will work only on kubelet 1.7.3+
# As the scrape endpoints for cAdvisor have changed
# if you are using older version you need to change the replacement to
# replacement: /api/v1/nodes/$1:4194/proxy/metrics
# more info here https://github.com/coreos/prometheus-operator/issues/633
relabel_configs:
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+)
- target_label: __address__
replacement: kubernetes.default.svc:443
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_name]
regex: (.+)
target_label: __metrics_path__
replacement: /api/v1/nodes/$1/proxy/metrics/cadvisor
# Scrape config for service endpoints.
#
# The relabeling allows the actual service scrape endpoint to be configured
# via the following annotations:
#
# * `prometheus.io/scrape`: Only scrape services that have a value of `true`
# * `prometheus.io/scheme`: If the metrics endpoint is secured then you will need
# to set this to `https` & most likely set the `tls_config` of the scrape config.
# * `prometheus.io/path`: If the metrics path is not `/metrics` override this.
# * `prometheus.io/port`: If the metrics are exposed on a different port to the
# service then set this appropriately.
- job_name: 'kubernetes-service-endpoints'
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape]
action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme]
action: replace
target_label: __scheme__
regex: (https?)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path]
action: replace
target_label: __metrics_path__
regex: (.+)
- source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port]
action: replace
target_label: __address__
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $1:$2
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_name
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_node
- job_name: 'prometheus-pushgateway'
honor_labels: true
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: service
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_probe]
action: keep
regex: pushgateway
# Example scrape config for probing services via the Blackbox Exporter.
#
# The relabeling allows the actual service scrape endpoint to be configured
# via the following annotations:
#
# * `prometheus.io/probe`: Only probe services that have a value of `true`
- job_name: 'kubernetes-services'
metrics_path: /probe
params:
module: [http_2xx]
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: service
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_probe]
action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__address__]
target_label: __param_target
- target_label: __address__
replacement: blackbox
- source_labels: [__param_target]
target_label: instance
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name]
target_label: kubernetes_name
# Example scrape config for pods
#
# The relabeling allows the actual pod scrape endpoint to be configured via the
# following annotations:
#
# * `prometheus.io/scrape`: Only scrape pods that have a value of `true`
# * `prometheus.io/path`: If the metrics path is not `/metrics` override this.
# * `prometheus.io/port`: Scrape the pod on the indicated port instead of the default of `9102`.
- job_name: 'kubernetes-pods'
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: pod
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape]
action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_path]
action: replace
target_label: __metrics_path__
regex: (.+)
- source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port]
action: replace
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $1:$2
target_label: __address__
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_name]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_pod_name
# adds additional scrape configs to prometheus.yml
# must be a string so you have to add a | after extraScrapeConfigs:
# example adds prometheus-blackbox-exporter scrape config
extraScrapeConfigs:
# - job_name: 'prometheus-blackbox-exporter'
# metrics_path: /probe
# params:
# module: [http_2xx]
# static_configs:
# - targets:
# - https://example.com
# relabel_configs:
# - source_labels: [__address__]
# target_label: __param_target
# - source_labels: [__param_target]
# target_label: instance
# - target_label: __address__
# replacement: prometheus-blackbox-exporter:9115
# Adds option to add alert_relabel_configs to avoid duplicate alerts in alertmanager
# useful in H/A prometheus with different external labels but the same alerts
alertRelabelConfigs:
# alert_relabel_configs:
# - source_labels: [dc]
# regex: (.+)\d+
# target_label: dc
networkPolicy:
## Enable creation of NetworkPolicy resources.
##
enabled: false
2. 설치 시 제공되는 데이터
NAME: air-kube-monitoring
LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Dec 10 05:16:50 2019
NAMESPACE: monitoring
STATUS: DEPLOYED
RESOURCES:
==> v1/ConfigMap
NAME AGE
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-alertmanager 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-server 0s
==> v1/DaemonSet
NAME AGE
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-node-exporter 0s
==> v1/Deployment
NAME AGE
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-alertmanager 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-kube-state-metrics 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-pushgateway 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-server 0s
==> v1/PersistentVolumeClaim
NAME AGE
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-alertmanager 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-server 0s
==> v1/Pod(related)
NAME AGE
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-alertmanager-544dc57d98-rvzl8 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-kube-state-metrics-f8b56557lkpj2 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-node-exporter-7rfhg 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-node-exporter-jzpnb 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-pushgateway-57d46489b5-kflhp 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-server-858f897974-2l4mt 0s
==> v1/Service
NAME AGE
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-alertmanager 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-kube-state-metrics 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-node-exporter 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-pushgateway 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-server 0s
==> v1/ServiceAccount
NAME AGE
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-alertmanager 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-kube-state-metrics 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-node-exporter 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-pushgateway 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-server 0s
==> v1beta1/ClusterRole
NAME AGE
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-alertmanager 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-kube-state-metrics 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-pushgateway 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-server 0s
==> v1beta1/ClusterRoleBinding
NAME AGE
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-alertmanager 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-kube-state-metrics 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-pushgateway 0s
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-server 0s
NOTES:
The Prometheus server can be accessed via port 80 on the following DNS name from within your cluster:
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-server.monitoring.svc.cluster.local
Get the Prometheus server URL by running these commands in the same shell:
export NODE_PORT=$(kubectl get --namespace monitoring -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}" services air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-server)
export NODE_IP=$(kubectl get nodes --namespace monitoring -o jsonpath="{.items[0].status.addresses[0].address}")
echo http://$NODE_IP:$NODE_PORT
The Prometheus alertmanager can be accessed via port 80 on the following DNS name from within your cluster:
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-alertmanager.monitoring.svc.cluster.local
Get the Alertmanager URL by running these commands in the same shell:
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace monitoring -l "app=prometheus,component=alertmanager" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
kubectl --namespace monitoring port-forward $POD_NAME 9093
#################################################################################
###### WARNING: Pod Security Policy has been moved to a global property. #####
###### use .Values.podSecurityPolicy.enabled with pod-based #####
###### annotations #####
###### (e.g. .Values.nodeExporter.podSecurityPolicy.annotations) #####
#################################################################################
The Prometheus PushGateway can be accessed via port 9091 on the following DNS name from within your cluster:
air-kube-monitoring-prometheus-pushgateway.monitoring.svc.cluster.local
Get the PushGateway URL by running these commands in the same shell:
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace monitoring -l "app=prometheus,component=pushgateway" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
kubectl --namespace monitoring port-forward $POD_NAME 9091
For more information on running Prometheus, visit:
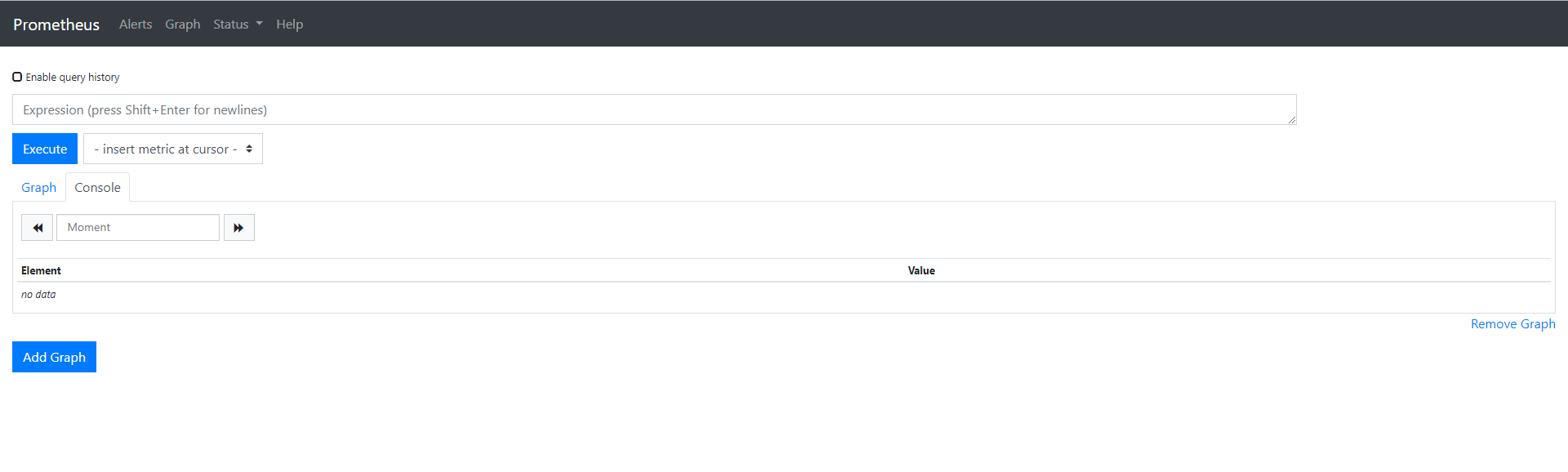
https://prometheus.io/2. 설치 확인
ip:port 접근하여 아래와 같이 접속되면 정상 동작입니다.
'Infra System' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Prometheus와 Grafana 연동 - Web UI Dashboard (0) | 2020.10.14 |
|---|---|
| Grafana installation - Web UI Dashboard (0) | 2020.10.14 |
| Authentication Server - Outer Architecture (0) | 2020.10.14 |
| Api-gateway Server - Outer Architecture (0) | 2020.10.14 |
| Eureka Server(standalone) - Outer Architecture (0) | 2020.10.14 |



댓글